Since the beginning of this year, the precipitation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River has been abnormally low, and some areas have experienced different degrees of drought, which has adversely affected agricultural production. From May 21 to 23, a large-scale rainfall process occurred in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. The soil moisture in the farmland was significantly improved, and the drought in some areas was moderated. However, the increase in water storage in Kutang was not obvious, and the agricultural water in the areas with less precipitation was still insufficient. It is estimated that from May 24 to 31, the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River will be dominated by sunny and hot weather, precipitation will still be less, and drought may continue or develop. It is recommended that all areas continue to prepare for drought relief, strengthen water and fertilizer management in farmland, and promote crop growth. development.
Analysis of the Influence of the Early Drought on the Agricultural Production in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River
Since the beginning of this year, the precipitation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River has continued to decrease, resulting in lower water levels in lakes, reservoirs, and ponds, and reduced water storage. Early rice tillers are slow and young spikes are affected. In the first season, rice paddy fields are insufficient for tillage, and dry crops are growing. Weak, cotton is difficult to transplant. According to the statistics of the Hubei Provincial Defense Office on the 20th, in addition to the Shennongjia forest area, there are droughts in 83 counties and cities in 16 other cities and counties. The area of ​​drought-affected farmland is 18.382 million mu, of which 874.1 million mu is drought in the field crops. 2,304,000 mu), water shortage of 8.629 million mu in paddy fields and 10.12 million mu in dry land; 780,000 people and 248,000 large livestock have difficulty drinking water; Danjiangkou Reservoir water level dropped to 134.7 meters, lower than the dead water level of 4.3 meters, the lowest in history The reservoir has a water storage capacity of only 5.57 billion cubic meters. The drought-affected area of ​​An Yi County in Jiangxi Province is 104.5 million mu, including 57,500 mu of light drought (36,000 mu of early rice and 21,500 mu of dry land) and 47,000 mu of heavy drought. 80% of the ponds in Hukou County are dry or semi-dry. A large number of livestock in rural areas have tight drinking water.
Analysis of the Influence of Precipitation Process on Agricultural Production in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River from May 21st to 23rd
From May 21 to 23, a large-scale precipitation process occurred in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. The rainfall was generally 10 to 25 mm, including eastern and southwestern Hubei, northern and western Hunan, north-central Jiangxi, southern Anhui, and central and northern Zhejiang. It is 30 to 50 mm, and it is 60 to 90 mm in the southeastern part of Hubei and parts of northwestern Jiangxi.
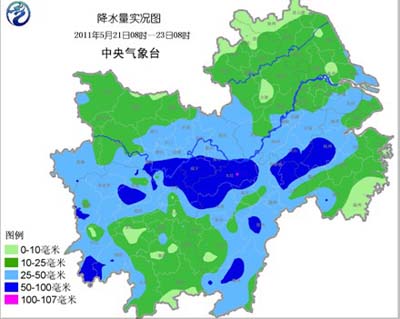
The precipitation time distribution is relatively uniform, which is conducive to the full penetration of water. The soil moisture in most farmland is improved significantly. The agricultural drought in the south of Jianghan and the northern part of the Yangtze River is obviously moderate, and the dryland area is reduced, which is conducive to the growth of cotton, corn and vegetables. It is supplemented by water. The live broadcast and transplanting water for one season is also effectively protected. However, precipitation has limited effect on reservoir and pond water storage, and the rice transplanting water in the first season is still insufficient. The comparison of the results of the statistical drought survey on May 22 and 20 in Hubei Province showed that the area of ​​drought-affected farmland decreased by about 5 million mu, and the area affected by the crops in the field decreased by 3 million mu (the area of ​​heavy drought decreased by 1.26 million mu), and the area of ​​water shortage in paddy fields. The reduction of 1.21 million mu and the reduction of dryland area by 800,000 mu.
With precipitation, from January 21 to 23, the temperature of the Japanese flat in the upper part of the Yangtze River and the Yangtze River, Jianghan, and the northern part of the Yangtze River fell to 13 to 19 °C, which inhibited the winter wheat grain filling in the Jianghuai and Jianghan areas to a certain extent, which was not conducive to increasing the grain weight, and would also cause the early rice in the south of the Yangtze River. The tillers are slow, and short spikes and small particles appear, affecting yield and quality.
Analysis of the impact of future weather on agricultural production in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
It is estimated that from May 24 to 31, the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River will be dominated by sunny and hot weather, with less rain. The precipitation along the Yangtze River is less than 10 mm, and the daily maximum temperature is between 32 °C and 36 °C. The drought in some areas may continue further. Or development. In the water-deficient areas, the rice transplanting water will be insufficient in the first season, and it will also affect the growth of dryland crops such as cotton and corn. Suggest:
1. The Jianghuai and Jianghan first-season rice areas should continue to actively carry out water storage and water conservation work to ensure timely transplanting of rice in a season; transplanted areas should be followed by application of seedling fertilizer and cultivation of strong and sturdy; Planting late-maturing varieties to ensure planting area.
2. The shallow water layer should be paid attention to in the early rice fields in the south of the Yangtze River. When the number of tillers reaches 75% to 80% of the effective number of spikes of the target yield, the field should be controlled according to local conditions, control of ineffective tillering, and prevention of pests and diseases.
3, cotton, corn and other dryland crops should seize the favorable moisture after the precipitation, timely transplant, timely fertilization, and promote normal growth.
Hand Drilling Rig,Concrete Building Tools,Wood Core Drill
Shanggong Power Tools Factory , http://www.ulite-powertools.com