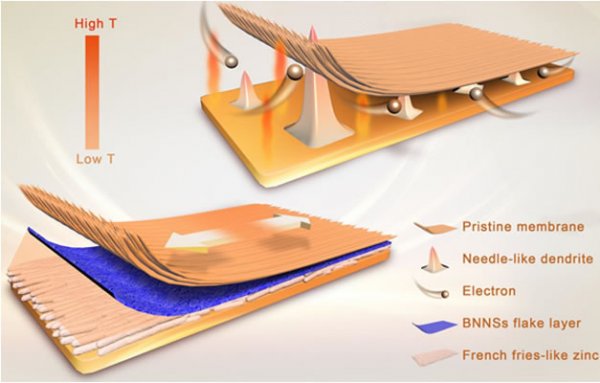
Recently, the researchers Li Xianfeng and Zhang Huamin of the Energy Storage Technology Research Department (DNL17), Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences have made new progress in the study of long-life zinc-based flow battery composite ion-conducting membranes.
ZFBs energy storage technology (ZFBs) energy storage technology has shown good application prospects in the field of distributed energy storage because of its low cost, high safety, and environmental friendliness. However, due to the problem of zinc dendrite / zinc accumulation, the development of such batteries is limited by poor cycle life and poor charge and discharge performance. The ion-conducting membrane can regulate the morphology of zinc deposition and inhibit the growth of dendrites, and plays an important role in improving the cycling stability of the battery. In the early stage, the research team found that through the charging characteristics of the membrane material, the zinc deposition direction and morphology can be adjusted, thereby greatly improving the surface capacity of the zinc-based flow battery and the cycle stability of the battery (Nat. Commun., 2018, 9 , 3731).
Based on the previous research work, this work introduced boron nitride nanosheets (BNNSs) with high thermal conductivity and high mechanical strength into the porous base membrane to prepare composite ion-conducting membranes. On the one hand, the BNNSs for the negative electrode can effectively improve the temperature distribution of the electrode surface and further adjust the zinc deposition morphology; on the other hand, its high mechanical strength can effectively prevent the excessive growth of zinc dendrites from damaging the membrane material. The synergy can significantly increase the cycle life of the battery. The alkaline zinc-iron flow battery assembled with the membrane was operated stably under the current density of 80 mA / cm2 for 500 charge-discharge cycles (nearly 800 h) without significant attenuation. Even at a current density of 200 mA / cm2, the energy efficiency exceeds 80%. The research results have important reference significance for the regulation of zinc anodes in zinc-based batteries.
Relevant research results were published in "German Applied Chemistry" (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.). The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation Project, Liaoning Natural Science Foundation Key Project, Shandong Province Major Science and Technology Innovation Project, Dalian Chemical Institute Independent Deployment Fund Project, etc.
Bench Drill is a compact size of the pillar drill that is designed for drilling holes through materials including a range of woods, plastics and metals. They are suitable for smaller holes or work pieces and have moderate to high speeds. The dills always come with a belt driver that makes it possible to select different speed: High speed for wood and lower speed for metal. In order to suit different size of projects, the height and angle of bench is adjustable.
Bench Drill
Bench Drill,Durable Drill Bench,Mini Bench Drill,Small Bench Drill
AWLOP CO.,LTD , https://www.awlop.com